With technology at our fingertips, the world is constantly evolving, as is how we shop. Whether for groceries, medicines, or even just a meal, the way we now shop has drastically evolved.
First came e-commerce, and as technology advanced, customer needs and expectations also changed.
Quick commerce and eCommerce have both changed the way we look and undertake purchasing goods and services.
But what do both quick commerce and eCommerce mean? Let’s look over the way commerce is undertaken today.
Here is what quick commerce and eCommerce offer you and how they are different.
What is eCommerce?
Ecommerce, often known as electronic commerce or online commerce, is the purchasing and selling of products and services through the internet. It also involves the financial and data transfers required to complete these transactions.
Ecommerce is frequently used to refer to the online sale of tangible goods. Still, it may also apply to any type of economic transaction made possible by the internet.
Types of eCommerce
When we think of e-commerce, we usually think of an online commercial transaction involving a supplier and a customer.
Ecommerce, to be more specific, can be divided into six major types, each with its own set of characteristics.
1. B2C or Business-to-Consumer
The establishment of electronic business relationships between businesses and final consumers distinguishes the Business-to-Consumer type of e-commerce. It corresponds to the retail e-commerce segment, where conventional retail trading takes place.
Compared to buying retail in traditional commerce, the consumer usually has more information available in terms of informative content. There is also a widespread belief that you will be able to buy for less money while still receiving equally personalized customer service as well as having your order processed and delivered quickly.
2. B2B or Business-to-Business
B2B e-commerce refers to all electronic transactions involving the exchange of products or services between businesses. Producers and conventional commerce distributors generally use this electronic commerce.
3. C2C or Consumer-to-Consumer
Consumer-to-Consumer e-commerce refers to all electronic transactions between consumers for products or services.
In most cases, these transactions are carried out through a third party, which offers the web platform on which the transactions are conducted.
4. B2A or Business-to-Administration
This section of e-commerce includes all online transactions between businesses and government agencies. This area encompasses a vast number of services in a range of fields, including fiscal, social security, employment, legal papers and records, and so on.
5. C2A or Consumer-to-Administration
All electronic transactions between people and government agencies are covered under the Consumer-to-Administration paradigm.
Both public administration models are intimately linked to the notion of government services providing citizens with efficiency and ease of use with information and communication technology.
6. C2B Consumer-to-Business
The typical concept of exchanging products is wholly reversed in consumer-to-business eCommerce.
In crowdsourcing initiatives, this form of e-commerce is particularly frequent. Many people sell their services or products to businesses that are specifically looking for these services or products.
Rise of eCommerce
In its first version, eCommerce was developed some 40 years ago. Since then, new technology, advancements in internet access, more security with payment gateways, and widespread consumer and corporate usage have helped innumerable enterprises expand.
Consumers went online in record numbers due to the COVID-19 pandemic throughout the world.
Ecommerce transactions totaled $82.5 billion in May 2020, up 77 percent from the previous year. Using steady year-over-year gains would have taken four to six years to reach that level.
Consumers turn to the internet to make purchases that they would regularly make in stores, such as food and household products, custom clothing, and entertainment.
Since the inception of CompuServe in 1969, eCommerce has gone a long way. Changes in technology, as well as worldwide situations, have fueled eCommerce expansion. Consumers’ expectations for safety and convenience have changed, and eCommerce must now satisfy those expectations.
Customers now have many options at their disposal, with each eCommerce business trying to get ahead of the competition by offering that little bit more. One such example is that of headless eCommerce platforms, which a lot of companies have recently adopted to provide customers with a swift and more personalized shopping experience.
Benefits of Quick Commerce and eCommerce
Ecommerce provides many benefits, including the ability to sell anywhere and creating personalized experiences that drive loyalty.
Let’s take a look at some of the advantages of eCommerce to better grasp between grasp how quick commerce and eCommerce differ in what they offer their users.
Most evidently, customers from all over the world may purchase on e-commerce sites, and businesses are no longer limited by location or physical obstacles.
Online shopping makes purchases easier, faster, and less time-consuming, with 24-hour sales, fast shipping, and simple returns.
E-commerce platforms may develop detailed user profiles that allow users to customize what they see and provide recommendations for other items they might like. There are different platforms for E-Commerce, but the key decisions will be whether you want to sell on a E-Commerce marketplace or your own shop, to learn more check out this Amazon vs Shopify guide.
This personalization enhances the customer experience by making customers feel understood personally, which increases the likelihood of brand loyalty.
Quick commerce, on the other hand, provides the following advantages to its customers:
Speed
When compared to traditional retail shops and eCommerce business models, q-commerce businesses may deliver items in a fraction of the time.
24-hour Operations
Like e-commerce, unlike brick-and-mortar businesses, dark stores are not restricted to fixed daily opening hours.
Guaranteed Product Availability
Thanks to investments in artificial intelligence and technology that monitor demand and alter inventories in real-time, things are more likely to be accessible.
Quick Commerce and eCommerce
Q-commerce is a new type of e-commerce that is faster. It combines the advantages of traditional e-commerce with advances in last-mile delivery.
As previously said, the fundamental distinction between quick commerce and eCommerce is the delivery time. Everything else is secondary to a company’s ability to deliver quickly.
While eCommerce offers delivery within a few hours at the most, quick commerce promises order fulfillment and delivery in minutes.
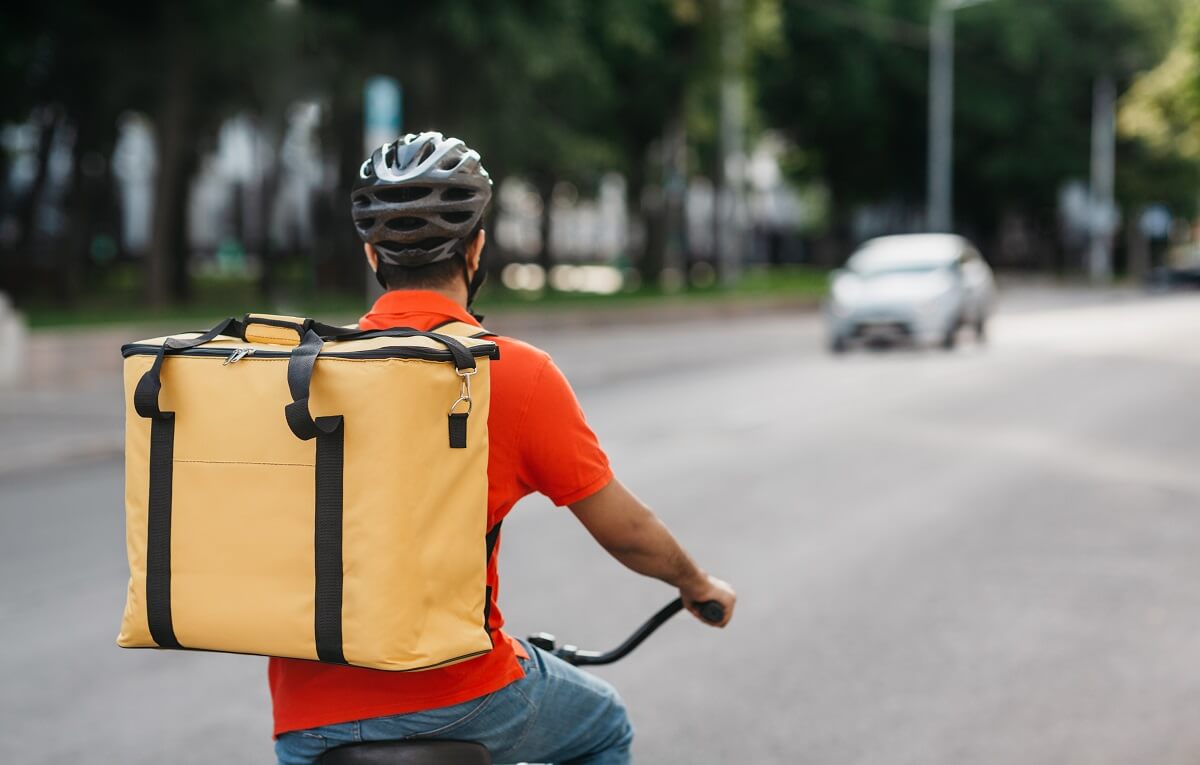
Another distinction is the delivery technique used by the two companies to deliver items to customers. Quick commerce enterprises use two-wheeled vehicles for delivery because of the desired speed such vehicles can offer.
Traditional e-commerce, on the other hand, frequently uses larger delivery vehicles as a form of products transportation.
In Q-commerce, dark storefronts are frequently used. These are fulfillment centers deliberately located in densely populated areas so that vehicles may quickly pick up and deliver things.
Another distinction is that quick commerce purchasing behavior is more of an impulsive buy from a psychological aspect.
eCommerce that has much longer shipping durations is painstakingly organized. As a result, the average cost per transaction is higher, and the variety of purchases is greater.
Another difference between quick commerce and eCommerce shoppers is that quick commerce purchasers are often younger. The demographic gap arises because young individuals are more likely to try out new services.
What is Quick Commerce
Q-Commerce, often known as quick commerce, is the next generation of eCommerce based on on-demand delivery. The company typically delivers the desired products within an hour of receiving the order.
The quick commerce business model combines the advantages of e-commerce (doing business over the internet) with conventional shopping (doing business in minutes) to produce a new business model that meets the growing need for speed while shopping online.
Characteristics of the Quick Commerce Business Model
The following characteristics distinguish the q-commerce business model from other eCommerce businesses:
Convenience
The most crucial characteristic of q-commerce is that it allows users to purchase whenever and wherever they want with a few simple taps on their phones.
Reduced Pricing
Q-commerce companies frequently buy in quantity, lowering the average cost of each good and allowing them to offer attractive discounts.
Instant Deliveries
An end-to-end technology stack built for highly optimized transactional and fulfillment speed.
Multi-Location Fulfillment Model
Location-specific inventory, trade areas, pricing, promotions, and analytics
Location-Based Ordering
Order and Delivery from nearby outlets for shorter delivery times.
Rise of Quick Commerce
No longer is it enough for eCommerce to deliver the shopping experience to your computer or phone. Quick commerce is the new face of eCommerce, catering to customers’ needs.
Everything falls under the umbrella of quick commerce, from food and beverage delivery to retail and grocery deliveries. The speed of delivery binds all of these distinct industries together; today’s modern customer wants their deliveries to arrive instantly.
According to a PwC study, efficiency and convenience were critical to delivering a stellar customer experience even before the onset of COVID-19. According to the same poll, 80 percent of US respondents felt these two qualities are critical to a pleasant overall experience.
The supply chain disruption caused by the Covid-19 pandemic increased eCommerce deliveries, and the necessity for faster delivery allowed quick commerce to flourish.
Quick commerce provided a unique business model in which products and services are delivered within 10-45 minutes of ordering.
Quick commerce is the new face of eCommerce, with it proving to be a game-changer in so many locations throughout the world.
To Summarize
Customers of a quick commerce-based company get swift service. Orders are processed and delivered at hyperspeed compared to traditional e-commerce, regardless of industry specialization.
In terms of service standards, the typical e-commerce approach, on the other hand, is inefficient. The usual shipping time is between 3 and 5 days, while larger purchases have their own set of delays. These problems still exist in several industries, but many organizations have begun to adopt quick commerce technologies due to Q-comm solutions.
Blink is a quick commerce enablement platform that can help move your business into the new world of eCommerce.
Blink provides you with online ordering solutions in the form of a branded website and mobile application to offer your customers the experience they deserve.
Blink isn’t only a go-to-market platform; it’s also meant to assist companies in increasing sales and profits.